|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 16(3); 2022 > Article |
|
See commentary "Letter to the Editor: Evaluating the Reproducibility of the Walking Test for Intermittent Claudication Associated with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis" in Volume 16 on page 611.
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the reproducibility of the walking test for patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
Overview of Literature
Walking test is one of the useful procedures to investigate cauda equina syndrome with lumbar spinal stenosis. One the other hands, there were few studies to investigate the reproducibility of this test.
Methods
In this study, we prospectively examined 70 LSS patients with intermittent claudication symptoms at a multicenter outpatient clinic. A walking test was administered at baseline and week 4 to assess patients’ walking distance and lower limb pain and numbness. Immediately after the walking test, patients were asked to use the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) to rate their pain and numbness in the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the lower legs. The reproducibility of the walking test was evaluated using Cohen’s κ analysis and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). Meanwhile, the Swiss Spinal Stenosis (SSS) Questionnaire was used to evaluate the severity of the stenosis.
Results
The walking distance ICC at baseline and at week 4 remained unchanged at 0.7, with acceptable interobserver reliabilities for lower limb pain and numbness in both legs. The average VAS score for lower leg pain was 23.2±25.2 mm at baseline and 27.4±28.8 mm at week 4, while the corresponding average VAS score for numbness was 23.4±26.7 mm at baseline and 24.8±25.2 mm at week 4. The ICC score was 0.7 for leg pain and 0.7 for numbness. The mean SSS was 30.2±5.5 at baseline and 29.2±5.2 at week 4, and there was no significant difference in the severity.
Intermittent claudication has been identified as a major symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) [1–3]. Along with standing and walking, increasing lumbar lordosis can affect the circumference of the cauda equina nerve, which can lead to ischemia. Thus, LSS patients commonly complain of pain or numbness in the legs. Symptoms of LSS after walking are difficult to detect in outpatient clinics. Previous research studies have reported the insufficiency of using radiography to assess patients at rest for cauda equina symptoms in LSS [4].
To adequately assess cauda equina symptoms, lower limb symptoms must be examined using a walking test. In addition, the treadmill test [5], bicycle test [6], and stoop test [7] can be used to detect ischemia in cauda equina. The bicycle test and the stoop test can detect cauda equina symptoms by having patients bicycle or flex their trunk back and forth. Although these two tests have proven useful for assessing patient functioning, they cannot assess the walking distance, walking time, and walking velocity that are considered important factors of gait. Thus, it is necessary to use the treadmill test to assess these factors. A previous study showed the walking test is superior to the treadmill test in terms of assessing leg symptoms with LSS, such as pain in the lower extremities and lower muscle weakness [8]. Patients’ symptoms of LSS are often intermittent and can change depending on activity, posture, and other factors, making it challenging for the physician to reliably detect these symptoms.
Therefore, a reproducible walking test is needed. However, few studies have compared the reproducibility of the assessments of intermittent claudication. Although Tomkins et al. [9,10] assessed the reproducibility of the walking test, the researchers assessed the reproducibility of distance only and did not assess the reproducibility of symptoms, velocity, or time. We believe the reason few studies have reported the reproducibility of the walking test is because physicians cannot repeat this test easily, particularly in an outpatient clinic. We believe that if the walking test’s reproducibility can be proven, this test can be used not only to assess the leg symptoms of LSS but also the treatment outcomes of LSS. Thus, we examined the test-retest reproducibility of the walking test for intermittent claudication associated with LSS.
This was a multicenter, prospective analysis of LSS patients. Patients with an established diagnosis of LSS based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) were eligible for study participation.
All patients were treated and evaluated as a large group. The study involved two types of patients with LSS: subjects who had not previously used any drugs and/or therapies for LSS and those who had used drugs and/or therapies for LSS. All subjects were treated with vitamin B12 upon initiation of the study. We asked the subjects who had previously been treated for LSS to discontinue their drug and/or therapy treatments to eliminate any interference from the treatments’ effects on LSS symptoms. However, those who chose to continue their treatments were asked to ensure the dosages and frequencies of their drugs and/or therapies were not changed during the study. Moreover, participants were not allowed to begin any new drugs or therapies for LSS during the study’s duration. In total, 80 patients diagnosed with LSS were enrolled in the study. Patients who fulfilled all of the following inclusion criteria were selected: (1) any gender, (2) age 20–80 years at the time of providing informed consent, (3) outpatient status, (4) a diagnosis of degenerative stenosis (central stenosis or degenerative spondylolisthesis) as per the international classification of bilateral intermittent claudication, (5) the ability to measure intermittent claudication distance at the beginning and end of the observation period, and (6) a degree of numbness in the lower extremities during walking at the start of observation. Meanwhile, the exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) positive results for the straight-leg-raising test; (2) a history of surgery for LSS; (3) lower leg numbness from cerebral palsy, brain infarctions, or diabetes mellitus neuropathy; (4) a disease affecting the gait (e.g., Parkinson’s disease, chronic arterial obstruction, metastatic spinal tumor, cervical myelopathy, and thoracic myelopathy); (5) a mental disease (e.g., depression); and (6) inability to understand the study’s purpose and processes. Of the total 80 subjects enrolled in the study, 10 dropped out after the baseline trial, while one subject did not meet the inclusion criteria. In addition, seven were excluded because of missing data in their baseline trial, and two subjects were lost to follow-up. Thus, 70 patients were enrolled for analysis. Table 1 summarizes the patients’ baseline characteristics.
All participants provided written informed consent for participation in the study and publication of their data, and the study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Peking Union Medical College Hospital (no., S-653), Peking University Third Hospital (no., 2014-32-II-GK), Military General Hospital, Command General Hospital, PLA General Hospital (no., 2014-056), The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (no., 2014909126), Xiangya Hospital Central South University (no., 201404035), Qilu Hospital of Shandong University (no., 2014-001), Guangzhou First People’s Hospital (no., 035), Xijing Hospital of No.4 Military Medical University (no number), Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (no. [2014]30), and Beijing Friendship Hospital Capital University of Medical Sciences (no., 2014-041).
The datasets generated and analyzed during this current study are not publicly available due to professional discretion, as they were part of patients’ records, but these can be made available as de-identified data sheets from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
We examined the following demographic variables: age (defined as the period from birth to the day informed consent was given, rounded to the nearest year), sex, height (first observation value), weight (first observation value), disease duration, comorbidity, medical history, symptom assessment (pain or numbness), and walking distance.
All subjects with LSS performed the walking test procedure as detailed in a previous report [8]. Subjects walked on flat ground without a cane or walker. The examiner walked parallel to the subjects without talking to them or entering their visual field and measured the walking distance and time. The subjects continued to walk until they were unable to walk any farther due to pain or numbness in the lower extremities. We then recorded each subject’s walking distance and subjective symptoms (location and magnitude of lower limb pain or numbness) in the walking test at baseline and at week 4. We assessed the location of patients’ pain or numbness by dividing the lower leg into the following five areas: the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the right and left legs (Fig. 1). Additionally, we used the Swiss Spinal Stenosis (SSS) Questionnaire to assess the severity of LSS. The SSS Questionnaire was devised to complement the existing generic measures of lumbar spine disability and health status in the evaluation of LSS patients. The questionnaire uses three scales to address patients’ severity of symptoms, physical function, and satisfaction after treatment. The five-item Physical Function Scale is used primarily to evaluate walking capacity by assessing the distance patients are able to walk and their ability to perform activities of daily living that involve walking [11,12]. To determine the reproducibility of the walking test, we administered the SSS Questionnaire at baseline and at week 4 and compared the data. Table 2 shows the schedule of this investigation.
We hypothesized the results of the walking test would remain unchanged from baseline to week 4 if the severity of LSS had not changed during the study period. Three statistical tests were used to assess the test-retest reproducibility. To assess intermittent claudication, the intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) was used to measure the interobserver agreement in documenting the walking distance. Meanwhile, Cohen’s κ analysis was used to assess the interobserver reproducibility of locating pain or numbness of the lower legs after walking. Meanwhile, the chi-square test was used to compare the degree of change on the SSS Questionnaire over a 4-week period. The data were then analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
The average walking distance was 467.8±551.3 m at baseline and 500.0±543.5 m at week 4. The ICC of the interobserver agreement of the walking distance between baseline and week 4 was 0.67 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.519–0.782), which indicates high reproducibility. Fig. 2 shows each subject’s walking distance at baseline and at week 4.
In the analysis of interobserver reproducibility for the location of lower limb pain, Cohen’s κ values were 0.5, 0.2, 0.5, 0.5, and 0.6 for the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the right leg, respectively. Similarly, Cohen’s κ values were 0.6, 0.4, 0.2, 0.7, and 0.6 for the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the left leg, respectively (Table 3).
In the analysis of interobserver reproducibility for the location of lower limb numbness, Cohen’s κ values were 0.3, 0.6, 0.5, 0.5, and 0.4 for the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the right leg, respectively. In a similar manner, Cohen’s κ values were 0.3, 0.5, 0.4, 0.5, and −0.0 for the front, back, outside, inside, and hip of the left leg, respectively (Table 4).
The average Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score for lower limb pain was 23.2±25.2 mm at baseline and 27.4±28.8 mm at week 4. The ICC of the VAS score for lower limb pain between baseline and week 4 was 0.668 (95 % CI, 0.515–0.780). The magnitude of lower limb pain demonstrated high reliability between baseline and week 4. Fig. 3 shows the walking distance of each subject at baseline and at week 4.
The average VAS score for lower limb numbness was 23.4±26.7 mm at baseline and 24.8±25.2 mm at week 4. The ICC of the VAS score for lower limb numbness between baseline and week 4 was 0.7 (95 % CI, 0.535–0.790). The magnitude of lower limb numbness demonstrated high reliability between baseline and week 4. Fig. 4 shows the walking distance of each subject at baseline and week 4.
This study evaluated the reproducibility of the walking test for intermittent claudication associated with LSS. Our results showed the walking test has acceptable reproducibility in terms of assessing the walking distance and the location and magnitude of lower limb pain and numbness. We then hypothesized the results of the walking test would remain unchanged from baseline to week 4 if the severity of LSS did not change during the study period. Because we asked the subjects who had previously been treated for LSS to discontinue their drug and/or therapy treatments to eliminate any interference from the treatments’ effects on LSS, there may have been a worsening in their walking ability resulting from treatment changes. However, we excluded patients who had severe radiculopathy caused by LSS; therefore, we considered the discontinuation of pain medications if it had little impact on the walking test.
The average SSS of subjects did not change significantly at week 4, which indicated the severity of subjects’ LSS had remained unchanged during the study period. Therefore, we believe our methods with respect to having patients stop or continue medications and/or other therapies did not affect the results of the walking test. The ICC of the VAS score for the magnitude of pain and numbness in the lower leg assessed using the walking test was 0.7, and Cohen’s κ coefficient of the location of lower leg numbness and pain was 0.2 to 0.6. Although this indicates a moderate correlation, most κ coefficients were about 0.5. Leg pain and numbness caused by LSS are often affected by the standing and walking posture or other factors, some of which remain unclear. Considering the characteristics of LSS, including its variable symptoms that are affected by several factors, we believe the test-retest reproducibility of the walking test is deemed acceptable. Therefore, it is possible to determine a patient’s symptoms to a certain extent by conducting the walking test at any time when their clinical symptoms have not subsided.
Intermittent neurogenic claudication has been determined to be caused by epidural pressure during walking [13]. Takahashi et al. [14] used an epidural transducer to examine the pressure in LSS patients’ epidural space; they concluded the epidural space pressure increased during walking and was higher in patients with LSS than in those without LSS. Amundsen reported that 95 of 100 patients with LSS showed intermittent claudication, which has been identified as a major symptom of LSS [4]. Thus, we believe it is crucial that physicians check for intermittent claudication associated with LSS to confirm patients’ reported symptoms.
The walking test, stoop test, cycling test, and treadmill test are used to detect intermittent neurogenic claudication [5–7,9,15–23]. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have compared these tests to show how well they assess the symptoms of LSS. Previous studies have compared the walking test and treadmill test in terms of assessing the leg symptoms of LSS patients for intermittent claudication [8,24]. Rainville et al. [24] had LSS patients perform the self-paced walking test and treadmill test before and after treatment. The authors stated the self-paced walking test was superior to the treadmill test in assessing the efficacy of LSS therapy [24]. Tanishima et al. [8] also had patients perform the walking test and treadmill test to assess LSS symptoms (root pain, cauda equina symptoms, and mixed symptoms) and concluded the walking test detected significantly more symptoms compared with the treadmill test. We agree the walking test is excellent for assessing the symptoms of LSS.
However, these investigations did not clarify reproducibility. Tanishima et al. [8] evaluated subjects’ symptoms using a one-time test, so reproducibility could not be evaluated. In addition, Rainville et al. [24] conducted their investigation without mentioning the reproducibility of the walking test. If the walking test has acceptable reproducibility, we can use it to evaluate LSS treatment outcomes. Therefore, we performed the walking test again at the 4-week mark to evaluate its reproducibility in assessing the symptoms of LSS. Patients’ medications and/or therapy treatments had not changed for 4 weeks, and the walking test showed an acceptable reproducibility in assessing LSS symptoms.
To examine the test-retest reproducibility for walking distance, Tomkins et al. [9] had LSS patients perform two self-paced walking tests. Patients walked until their LSS symptoms required them to sit down and rest. The researchers reported a test-retest ICC of 0.9 for the distance walked. Another study reported an ICC of 0.7 for the walking distance in the walking test [10]. These studies revealed only the test-retest reliability for the walking distance without examining other factors, such as the location or magnitude of lower limb pain or numbness in the walking test. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to clarify the reproducibility of not only the walking distance but also the location and magnitude of lower leg symptoms measured in the walking test. Thus, we believe the walking test is a useful method to assess the clinical status of patients’ LSS.
There are some limitations to use the walking test for assessing LSS patients’ leg symptoms. To our knowledge, no studies have reported the test’s responsiveness without measuring the walking distance; this is a major reason we attempted to demonstrate the test-retest reproducibility of the walking test for intermittent claudication associated with LSS. We set the interval to investigate the test-retest reproducibility of the walking test at 4 weeks in our study. This interval may be considered too long to assess the reproducibility of any statistical test of physical assessment. Generally, most physicians evaluate the efficacy of drug therapy or other treatments over at least 4 weeks. We believe our assessment of the reproducibility of the walking test at the 4-week mark shows this test is an excellent tool for investigating the treatment outcomes of any procedures, such as drug therapy, rehabilitation, or surgery.
This study had certain limitations. First, among the subjects who had LSS we enrolled, we did not distinguish between subjects with single-level stenosis and those with multilevel stenosis. Additionally, we did not record the grading or radiological severity of LSS. It is necessary to enroll subjects with the same level of stenosis to ensure the accuracy of the findings. Second, we did not use an imaging modality, such as MRI, CT, or radiography, to assess patients’ lower limb symptoms. Third, although we decided to perform only a single follow-up at week 4 to clarify the reproducibility of the walking test in terms of assessing walking distance and location and magnitude of lower leg pain and numbness in this study, a longer follow-up duration of 8 or 12 weeks may be required to determine the test’s true reproducibility.
This study has evaluated the reproducibility of the walking test for LSS patients. As per our findings, the walking test showed an acceptable reproducibility for assessing the walking distance and the location and magnitude of lower leg symptoms. The walking test showed similar results to those obtained in situations where the severity of LSS remained unchanged. Thus, this test can be considered a useful method in evaluating LSS treatment outcomes. In particular, the reproducibility of the walking test in pinpointing the location of pain and numbness in the lower leg indicates that physicians can use the walking test in identifying patients’ symptoms of LSS.
Conflict of Interest
ST received funding support by Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Qiu Guixing, Dr. Li Shugang, Dr. Sun Tiansheng, Dr. Zheng Yanping, Dr. Zhang Guangming, Dr. Iuo Zhuojing, and Dr. Wang Bingqiang for their advice regarding study design and search strategy.
Fig. 1
The schema of the lower limb. a: in front of the leg; b: back of the leg; c: outside of the leg; d: inner side of the leg; and e: hip.
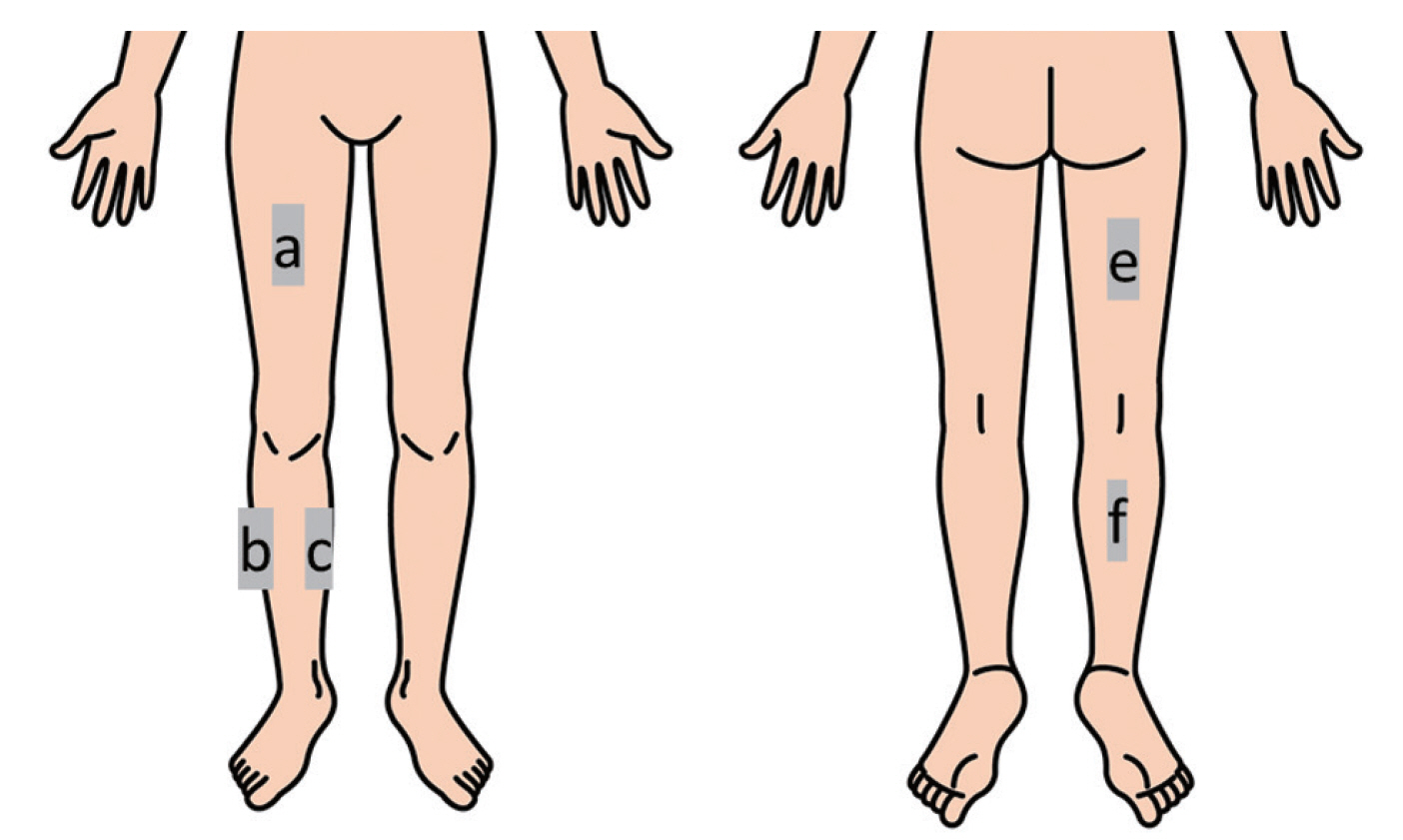
Fig. 3
This graph shows the magnitude of lower limb pain at baseline and at week 4 using the Visual Analog Scale.
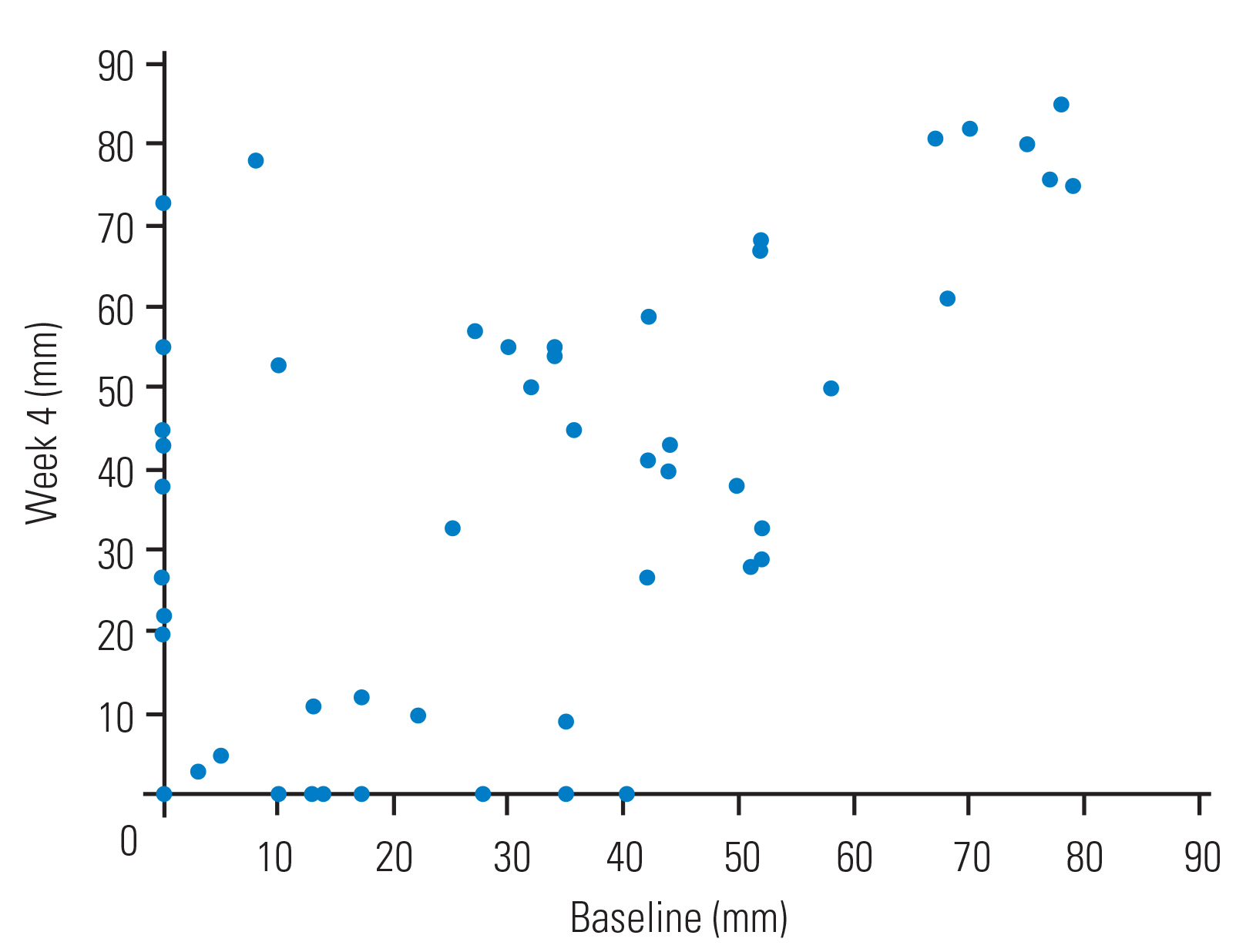
Fig. 4
This graph shows the magnitude of lower limb numbness at baseline and at week 4 using the Visual Analog Scale.
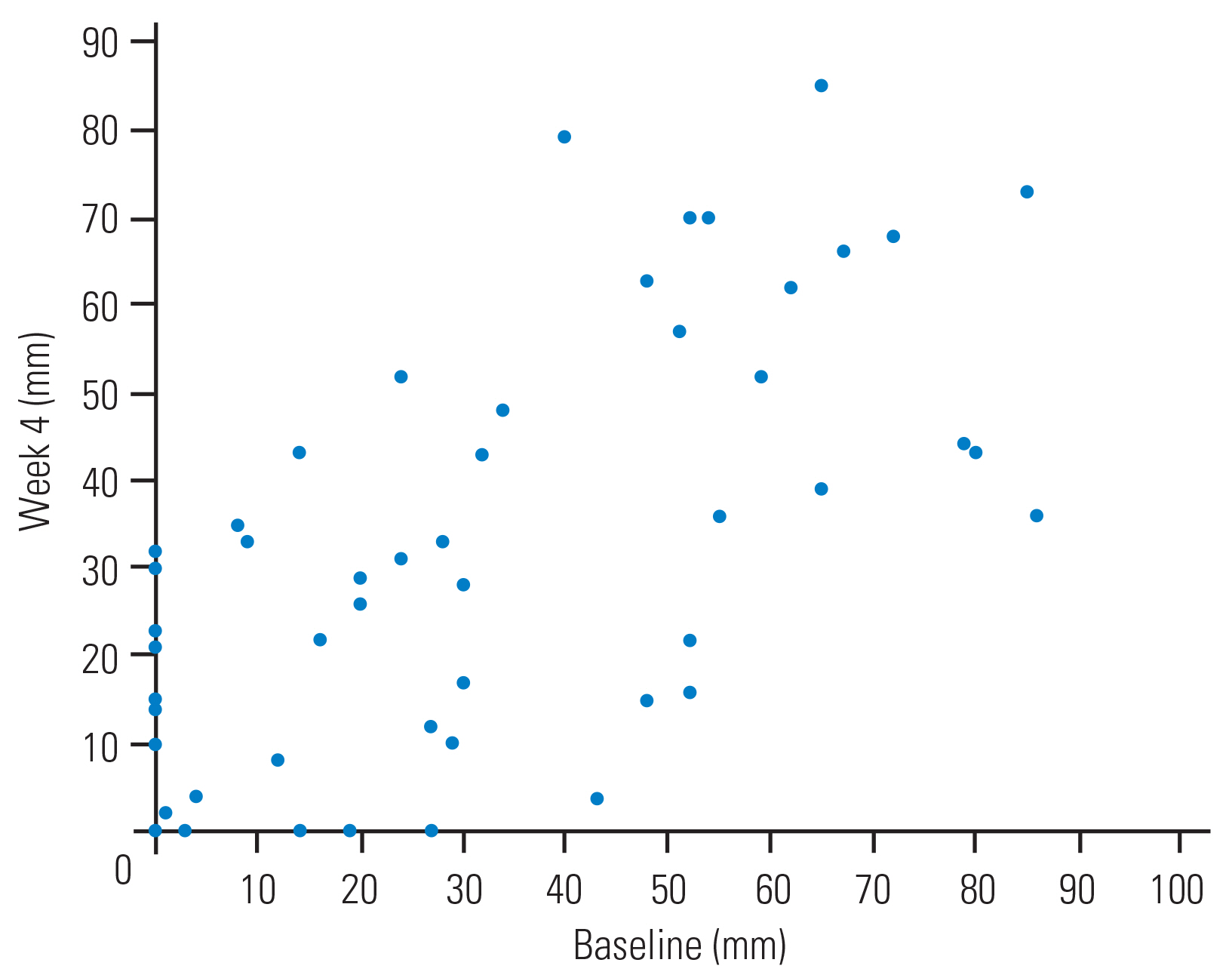
Table 1
Demographic variables
Table 2
Study schedule
Table 3
Reproducibility analysis for lower limb ache after walking
Table 4
Reproducibility analysis for lower limb numbness after walking
References
1. Verbiest H. Pathomorphologic aspects of developmental lumbar stenosis. Orthop Clin North Am 1975;6:177–96.


2. Schatzker J, Pennal GF. Spinal stenosis, a cause of cauda equina compression. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1968;50:606–18.


3. Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Paine KW, Cauchoix J, McIvor G. Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1974;(99): 30–50.
4. Amundsen T, Weber H, Lilleas F, Nordal HJ, Abdelnoor M, Magnaes B. Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical and radiologic features. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1178–86.

5. Padmanabhan G, Sambasivan A, Desai MJ. Three-step treadmill test and McKenzie mechanical diagnosis and therapy to establish directional preference in a patient with lumbar spinal stenosis: a case report. J Man Manip Ther 2011;19:35–41.



6. Dyck P, Doyle JB Jr. “Bicycle test” of van Gelderen in diagnosis of intermittent cauda equina compression syndrome: case report. J Neurosurg 1977;46:667–70.

8. Tanishima S, Fukada S, Ishii H, Dokai T, Morio Y, Nagashima H. Comparison between walking test and treadmill test for intermittent claudication associated with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Eur Spine J 2015;24:327–32.


9. Tomkins CC, Battie MC, Rogers T, Jiang H, Petersen S. A criterion measure of walking capacity in lumbar spinal stenosis and its comparison with a treadmill protocol. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:2444–9.


10. Tomkins-Lane CC, Battie MC. Validity and reproducibility of self-report measures of walking capacity in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:2097–102.


11. Tomkins CC, Battie MC, Hu R. Construct validity of the physical function scale of the Swiss Spinal Stenosis Questionnaire for the measurement of walking capacity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1896–901.


12. Stucki G, Daltroy L, Liang MH, Lipson SJ, Fossel AH, Katz JN. Measurement properties of a self-administered outcome measure in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:796–803.


14. Takahashi K, Kagechika K, Takino T, Matsui T, Miyazaki T, Shima I. Changes in epidural pressure during walking in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:2746–9.


15. Deen HG Jr, Zimmerman RS, Lyons MK, McPhee MC, Verheijde JL, Lemens SM. Measurement of exercise tolerance on the treadmill in patients with symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a useful indicator of functional status and surgical outcome. J Neurosurg 1995;83:27–30.


16. Kim YS, Park SJ, Oh IS, Kwan JY. The clinical effect of gait load test in two level lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J 2009;3:96–100.



17. Herno A, Airaksinen O, Saari T. Computed tomography after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: patients’ pain patterns, walking capacity, and subjective disability had no correlation with computed tomography findings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994;19:1975–8.

18. Dong G, Porter RW. Walking and cycling tests in neurogenic and intermittent claudication. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989;14:965–9.


19. Fritz JM, Erhard RE, Delitto A, Welch WC, Nowakowski PE. Preliminary results of the use of a two-stage treadmill test as a clinical diagnostic tool in the differential diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 1997;10:410–6.


20. Herno A, Airaksinen O, Saari T, Pitkanen M, Manninen H, Suomalainen O. Computed tomography findings 4 years after surgical management of lumbar spinal stenosis: no correlation with clinical outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1999;24:2234–9.


21. Whitehurst M, Brown LE, Eidelson SG, D’angelo A. Functional mobility performance in an elderly population with lumbar spinal stenosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2001;82:464–7.


22. Moon ES, Kim HS, Park JO, et al. Comparison of the predictive value of myelography, computed tomography and MRI on the treadmill test in lumbar spinal stenosis. Yonsei Med J 2005;46:806–11.