|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 16(4); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Predictive clinical and radiological factors can potentially identify adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) most likely to benefit from overcorrection nighttime bracing. These factors can provide helpful information in clinical decision making. However, the relationship between these factors and outcomes of overcorrection nighttime bracing is unclear. This systematic review determined the predictive factors for identifying outcomes of overcorrection nighttime bracing in AIS. A systematic search was conducted on PubMed, MEDLINE, Scopus, and Embase from January 1986 to January 2021. Studies on AIS patients, aged 10–18 years, with a Risser sign of 0–2 and an initial Cobb angle of 20°–45°, who were treated with overcorrection nighttime bracing and for whom at least one predictive factor of treatment outcome (failure and/or success) was assessed were included. Two blinded reviewers independently evaluated the studies using a quality assessment tool. To determine predictive factors, the level of evidence was rated through best-evidence synthesis. A total of nine studies met the inclusion criteria. A Providence brace was used in six of the included studies, while a Charleston bending brace was used in three. Findings from two high-quality studies provided strong evidence of the association between curve flexibility and brace treatment success. In terms of the Risser sign, this evidence was obtained from three high-quality studies. Moderate evidence indicated a positive association between premenarchal status and nighttime bracing failure. Inconclusive evidence indicated that poor brace compliance is associated with treatment failure. Conflicting evidence of treatment failure was indicated for initial curve magnitude, curve type, in-brace correction, age, Risser sign, curve apex, and sex. These findings show that greater curve flexibility and a higher Risser sign are associated with overcorrection nighttime bracing success.
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a growth-related pathology of the spine in which a series of vertebrae become deformed in all three planes of motion [1]. In 90% of cases, this deformity manifests during adolescence; however, its etiology is unknown [2]. The prevalence of AIS is reportedly between 0.47% and 5.2% in individuals aged 10–16 years [2].
Although the exact cause of the onset of scoliosis is unknown, the determinants responsible for its progression are well known and are classified into growth-related factors and curve characteristics. These determinants include timing of peak height velocity [3], chronologic age, a Risser sign of 0–2, and a curve magnitude of >30° [4]. In growing adolescents with mild to moderate curves of 20°–45°, full-time bracing is a widely accepted, nonsurgical intervention aimed at limiting further progression of the curve, decreasing the rate of surgical intervention [5,6]. Compliance with full-time bracing intervention is negatively affected by physical discomfort and psychosocial factors, including peer-pressure during school hours [7].
Overcorrection nighttime bracing has been introduced as an alternative to full-time bracing to address these concerns [8,9]. Overcorrection nighttime braces were developed based on the concept that part-time brace use may be effective [10–13]. For the first time, Green [12] reported that part-time treatment with a Boston or a Milwaukee brace (16 hr/day) can produce good outcomes and that the regimen of full-time bracing is unnecessary. Emans et al. [11] concluded that wearing a Boston brace part-time is as successful as wearing it full-time. Moreover, the effectiveness of wearing a Wilmington brace part-time is the same as wearing it full-time [10]. Peltonen et al. [13] reported that the outcomes for patients who worn a Boston brace for 12 hr/day were the same as those for patients who wore their braces for 23 hr/day. The mechanism of action of these braces creates a 3-point pressure system to provide a mechanical constraint at the location of the curve [14,15]. The current alternative to part-time bracing in AIS is overcorrection nighttime bracing. Worn during the night for only 8–10 hours, overcorrection nighttime braces are developed to benefit from the recumbent position to move the scoliosis curve as closely as possible against the midline. Because of the vigorous forces that these braces apply, they cannot be worn when the patient is upright and can be worn only when the patient is recumbent [16].
The long-term effectiveness of overcorrection nighttime bracing has equivalent efficacy to full-time bracing [17], and the negative effects of overcorrection nighttime braces are minimal [18]. Overcorrection nighttime bracing may be indicated in cases where full-time bracing compliance is low [17,19]. The Charleston bending brace [9,20] and the Providence nocturnal design [8,21] are the most common overcorrection nighttime braces in the treatment of AIS. These braces are worn in the recumbent position for 8–10 hr/day and apply lateral and de-rotational forces to the trunk, resulting in improved spinal alignment [21,22]
A lack of in-brace correction (IBC), poor brace compliance, a low level of skeletal maturity, and an initial Cobb angle of >30° are the main potential predictive factors for failure of full-time bracing [23,24]. Ruffilli et al. [17] found no difference in the failure rate between full-time and overcorrection nighttime bracing for AIS. Predictive factors such as clinical and radiological characteristics could potentially identify individuals most likely to benefit from this intervention [25]. These predictive factors could provide information helpful in clinical decision making with regard to the use of overcorrection nighttime bracing as an alternative strategy for AIS. However, the predictive factors for overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes in AIS have not yet been reported. Therefore, this systematic review assessed the most important clinical and radiological parameters predictive of the outcomes of overcorrection nighttime bracing in AIS.
A computerized systematic search was conducted on PubMed, MEDLINE, Scopus, and Embase from January 1986 to January 2021 using the following search terms: (((((idiopathic [Title/Abstract]) AND (scoliosis [Title/Abstract])) AND (brace [Title/Abstract])) OR (bracing [Title/Abstract])) AND (nighttime [Title/Abstract])) OR (part-time [Title/Abstract]).
In addition, reference lists of all included articles were screened by two reviewers to identify other potential studies relevant to this systematic review. Only articles written in English were included. The review was registered in PROSPERO (ID: CRD42020179767).
Title and abstract screening was independently performed by the two reviewers, and potentially relevant articles were selected. The two reviewers then independently performed a full text review based on inclusion/exclusion criteria. Any discrepancy between the reviewers was resolved by a consensus meeting or by consulting a third reviewer.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: individuals diagnosed with AIS, age 10–18 years, Risser sign of 0–2, Cobb angle of 20°–45° at initiation of bracing, treatment with overcorrection nighttime bracing, no other previous treatment, and at least one predictive factor of treatment outcome (failure and/or success) assessed. Articles were included if bracing continued until the end of skeletal maturity or spinal fusion. Studies that evaluated the efficacy of full-time bracing or included AIS/juvenile idiopathic scoliosis and other types of scoliosis other than idiopathic were excluded. Review articles, case reports or case study designs, and conference abstracts were also excluded.
The following data were extracted from the included studies: study design, number of patients, age at initiation of bracing, initial Risser sign, initial curve magnitude, curve type, type of brace, IBC, brace treatment length, follow-up duration, and definition for treatment failure and success (Table 1).
Two reviewers independently evaluated the studies using the method developed by Hayden et al. [26] and suggested by Lievense et al. [27] and Scholten-Peeters et al. [28]. This method consists of 13 items categorized into five domains (Table 2). A criteria list was prepared to assess the methodological quality of prediction studies. The score of each item was 0 (missing or insufficient data) or 1 (sufficient data reported). Average scores for the quality assessment tool ranged from 0 (lowest) to 13 (highest). Score cut-offs of ≥9 and <9 indicated high and low-quality, respectively (Table 3). A similar method of quality assessment was used to systematically review observational studies on predictive factors for full-time brace treatment outcome in AIS [23], prognostic factors for curve progression in degenerative lumbar scoliosis [29], prognostic factors of progression of knee and hip osteoarthritis [27,30], and predischarge prognostic factors of physical function in older adults with hip fracture surgery [31]. Scoring disagreement was resolved by discussion or by consulting a third reviewer.
To determine the predictive factors for the effectiveness of nighttime bracing in AIS, the level of evidence of each factor was rated using best-evidence synthesis [32]. The evidence was considered strong in the case of consistent findings in multiple (≥2) high-quality studies, moderate for findings reported in one high-quality study and multiple (≥2) low-quality studies, limited for findings in one high-quality study or consistent findings in ≥3 low-quality studies, inconclusive for findings in ≤3 low-quality studies, and conflicting for consistent findings in <75% of the studies.
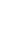
The results of the research are summarized in Fig. 1. After removing duplicates and irrelevant articles, 61 papers remained. After evaluating the full text of these papers, nine studies met the eligibility criteria for this systematic review.
Table 1 presents the characteristics of the nine eligible studies. Overcorrection nighttime bracing was defined as brace wearing for 8–10 hours during the night. The sample size of included studies was 34–166 patients, with a total sample of 675. The brace wearing time was 12–40 months, and the follow-up period varied between 12 and 130 months. In six studies, the device was a Providence brace, whereas in three studies, it was a Charleston bending brace. Curve progression of >5° and ≤5° was defined as a treatment failure and success, respectively.
The studies considered various factors as potential predictors for brace treatment outcome, classified as radiographic or clinical characteristics. Of the nine studies, most (six studies) did not report the results of regression analysis. As a result of heterogeneity of studies, pooling was not possible (Table 4).
Two high-quality studies suggested a strong evidence of an association between curve flexibility [8,35] and brace treatment success. Three high-quality studies suggested strong evidence of an association between the Risser sign [8,33,34] and brace treatment success. The curve progression among patients with Risser signs of 0 and 1 was higher than those with a Risser sign of 2. The evidence for curve type was inconclusive.
Davis et al. [33] divided participants into two groups based on the Risser sign (0 and ≥1). A curve progression rate of <5° in the group with Risser sign ≥1 was 78.6% compared with 40% for the group with Risser sign=0. Results suggested that when combining the Risser sign of ≥1, initial Cobb angle of <35°, and curves with an apex at T10 or lower, the success of overcorrection nighttime bracing is 100% for AIS patients if all these parameters exist, 64% for two of three parameters, 25% if one parameter exists, and 0% when none of the parameters exists. D’Amato et al. [8] found that the success rate of treatment for patients with Risser sign=0 is significantly lower (67%) than for those with Risser sign=1 or 2 (86% or 83%, respectively). However, Lee et al. [38], in a low-quality study, found no significant differences between the brace success rate among patients with a Risser sign of 0–2. The results of three high-quality studies [8,33,34] and one low-quality study [39] revealed that the degree of IBC is associated with the success of overcorrection nighttime bracing. In contrast, one high-quality [33] and one low-quality [41] study found no association between IBC and the success of overcorrection nighttime bracing.
Katz et al. [34] reported that when the IBC is >80%, the probability of successful brace treatment is significantly greater compared to an IBC of <80% (p=0.006). Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] found that the IBC for patients with successful and failed Providence brace treatment is 66% and 53%, respectively. Overall, the evidence for IBC was inconclusive.
In two high-quality studies [33,34], strong evidence indicates a negative association between the Risser sign and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. In one high-quality study [35], moderate evidence indicates a positive association between premenarchal status and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. According to univariate linear regression analyses, the failure of the Providence brace was significantly correlated with low flexibility and premenarchal status. R2 was 0.23 for flexibility and reached 0.39 by adding menarchal status. Only one low-quality study evaluated brace compliance as a predictive factor for treatment outcome [37]. The evidence suggesting that poor brace compliance is associated with treatment failure was inconclusive. The evidence of treatment failure indicated for initial curve magnitude, curve type, IBC, age, Risser sign, curve apex, and sex was conflicting (Table 4).
In a high-quality study on 102 adolescents with AIS with curves between 20° and 42°, D’Amato et al. [8] found that in cases with a curve of >35°, 77% of patients treated with a Providence brace experienced curve progression of >5°. In cases with a curve of <35°, 34% of patients experienced curve progression of >5°. Davis et al. [33], in their high-quality study, found that the initial curve magnitude was inversely related to Providence bracing success when the curve was between 25° and 40°. They divided patients into two groups based on curves of <35° and >35°. Patients with a curve of <35° experienced a 70% success rate, while those with a curve of >35° had a 41% success rate. Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] and Lee et al. [38] found no relationship between the initial curve magnitude and overcorrection nighttime bracing success.
This study identified predictive factors for the effectiveness of overcorrection nighttime bracing in AIS. The results of nine included studies were evaluated according to best-evidence synthesis. Among six radiological and four clinical predictive factors, strong evidence indicates that curve flexibility and the Risser sign are two main factors for overcorrection nighttime bracing success. Additionally, moderate evidence indicates that premenarchal status is associated with bracing failure.
Curve flexibility evaluation provides guidance related to therapeutic plans, so it is essential in AIS treatment [42–44]. Measuring curve flexibility is also important for estimating the bracing outcome in AIS. Because patients with greater flexible curves experience a higher IBC, curve flexibility may affect the final outcome of bracing [35,45]. The results of this systematic review suggest that there is strong evidence of a positive association between curve flexibility and overcorrection nighttime bracing success [8,35]. However, limited evidence indicates no association between curve flexibility and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. Failure of overcorrection nighttime bracing may increase if the patient has low flexibility and premenarchal status. Various techniques of evaluating curve flexibility have been proposed, such as supine lateral bending radiographs (SLBRs), supine, prone, sitting with lateral bending, prone with lateral bending, and fulcrum-bending radiographs [36,42,46]. However, there is a lack of consensus among researchers about which method of assessing flexibility is the best. He and Wong [46] measured spinal flexibility in the following positions: prone, supine, sitting with lateral bending, and prone with lateral bending. The found that the prone position is the best for measuring the flexibility of the spine [46]. Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] assessed curve flexibility in a Providence brace using the SLBR method and defined it as [(Cobb angle in standing position–Cobb angle in supine lateral bending position)/Cobb angle in standing position]×100. The authors found that curve flexibility can be an important predictive factor for the outcome of using a Providence brace in AIS. In contrast, some researchers have found that the SLBR method depends on the patient’s effort and the radiologist’s expertise, which limits the method’s reliability and constancy [42,47,48]. Moreover, if a patient has low back pain, the accuracy of the test might decrease because of failure to use high forces [47]. Future studies on this topic are therefore recommended.
We found strong evidence of an association between a high Risser sign and overcorrection nighttime bracing success. The association between this factor and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure was also strong [33,34]. The Risser sign is generally applied as a maturity index in AIS with reference to iliac apophysis ossification. However, due to the radiographic parallax, it is less apparent on postero-anterior radiographs. Moreover, the Risser sign can be distinguished after the peak height velocity, it is not a good index for evaluating the amount of growth remaining, and it correlates differently in boys than in girls [3,49]. To determine accurate maturity during adolescence, Sanders et al. [50] developed a reliable skeletal maturity scoring system based on patterns of the digital skeletal age of the hand. These patterns are highly correlated with the peak height velocity. None of the studies included in this systematic review used the Sanders system. Further studies that take this variable into account to determine the success or failure of overcorrection nighttime bracing in AIS need to be undertaken.
According to a high-quality study by Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35], moderate evidence indicates that premenarchal status is associated with Providence brace failure. The definition of evidence used in our review is similar to that used by van den Bogaart et al. [23]. However, based on their results, inconclusive evidence suggests that menarchal status is not associated with full-time bracing failure [23]. Further studies that measure premenarchal status should be undertaken to develop a full understanding of the impact of this variable on the outcome of overcorrection nighttime bracing in AIS.
IBC, which describes the difference between the in-brace Cobb angle and the initial out-of-brace Cobb angle, is one of the main factors for the long-term efficacy of full-time bracing [23,24]. Studies have reported a strong relationship between a lack of IBC and full-time bracing failure [23,24]. However, in our review, the evidence of the success or failure of overcorrection nighttime bracing being related to IBC was inconclusive and conflicting. A possible explanation could be differences in IBC measurement methodologies. Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] measured IBC as [(Standing out-of-brace Cobb angle–standing in-brace Cobb angle)/standing out-of-brace Cobb angle]×100. D’Amato et al. [8] and Simony et al. [39] measured IBC as [(standing out-of-brace Cobb angle–supine in-brace Cobb angle)/standing out-of-brace Cobb angle]×100. In contrast, Trivedi and Thomson [41] measure IBC as [(standing out-of-brace Cobb angle–prone in-brace Cobb angle)/standing out-of-brace Cobb angle]×100. These differences in methodology make it difficult to determine whether a higher IBC is due to more flexible and therefore correctible curves or better fitting of the brace.
Initial curve magnitude is calculated from the Cobb angle at the initiation of brace treatment. Overcorrection nighttime bracing is most effective when the initial curve is <35° [8,34]. Five high-quality studies [8,33–35,51] and four low-quality studies [37–40] on adolescents with initial curves of 20° to 45° revealed conflicting evidence associating the initial curve magnitude and overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes.
There is conflicting evidence regarding the association between the initial curve magnitude and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. Simony et al. [39] and Davis et al. [33] found that a higher initial curve magnitude is associated with a higher rate of Providence nighttime brace failure, while Bohl et al. [37] and Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] concluded that there is no association between the initial curve magnitude and Providence nighttime brace failure. According to a systematic review by van den Bogaart et al. [23], moderate evidence indicated that the initial curve magnitude is not correlated with full-time bracing failure.
We found conflicting evidence of a relationship between curve apex and overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure. A high-quality study suggested that for curves with an apex at T10 or lower, the overcorrection nighttime bracing success rate is significantly higher than for curves with an apex at T6–T9 (69.4% versus 40.6%, respectively) [33]. In another high-quality study of patients treated with a Providence brace [8], the treatment success rate was 79% for those with a curve apex of <T8 and 61% for those with a curve apex >T8. Two low-quality studies by Lee et al. [38] and Bohl et al. [37] found no significant relationship between the curve apex and overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure.
Curve type is considered a risk factor for bracing failure in AIS [52]. Hawary et al. [24] suggested that the type of curve is a potential risk factor for full-time bracing failure. Preliminary studies on the effectiveness of overcorrection nighttime bracing have hypothesized that these braces are more effective for single lumbar or thoracolumbar curves than for double or thoracic curves [34,40,53]. However, our results found that the evidence of an association between overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure and curve type is inconclusive and conflicting. In high-quality studies by Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] and Katz et al. [34], double major curves and single thoracic curve types were identified as a risk factor for overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. Additionally, in high- and low-quality studies [33,37], no relationship was found between curve type and Providence nighttime bracing failure. Furthermore, two published studies have reported that curve type has no significant relationship with Charleston nighttime bracing success [38,41].
The evidence of a relationship of age and sex with overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure is conflicting. This finding is consistent with that of van den Bogaart et al. [23], who reported conflicting evidence of an association between full-time bracing failure and age and sex.
The role of this parameter in the outcome of overcorrection nighttime bracing has not received much attention and has been evaluated only in one low-quality study [37]. Evidence of an association of poor brace compliance with overcorrection nighttime bracing failure is inconclusive. Compliance with brace wearing may be an important predictive factor for the effectiveness of full-time bracing. Hawary et al. [24] found that a lack of brace compliance is a primary factor for full-time bracing failure. Additionally, moderate evidence indicates that poor brace wearing is associated with full-time bracing failure [23]. Future studies should continue to objectively examine the relationship between compliance and overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure.
This systematic review had several limitations that need to be considered when interpreting the results. First, strong evidence indicates that increased curve flexibility and a higher Risser sign are associated with overcorrection nighttime bracing success. However, the number of studies evaluating the role of flexibility and skeletal maturity in overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes in AIS is insufficient. Future studies are therefore recommended. Second, studies evaluating predictive factors for overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes in AIS are few. In this systematic review, we highlighted the importance of all radiologic and clinical parameters that potentially may play a role in overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes. However, some questions remain. Therefore, additional longitudinal studies are needed to assess all potential predictive factors for overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes. Third, the heterogeneity of the measurement methodology of variables, definitions of treatment outcomes, the process of evaluation, and the manner of reporting results, across the included studies, precluded the ability to perform a meta-analysis. Fourth, the results only included articles published in English. Perhaps including studies in other languages would alter the results. Finally, our conclusions are based on statistics of retrospective studies that are prone to numerous prejudices that may indicate differences noticed between predictive factors and overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes.
Strong evidence indicates that increased curve flexibility and a higher Risser sign are associated with overcorrection nighttime bracing success. Additionally, moderate evidence indicates a negative association between premenarchal status and overcorrection nighttime bracing failure. Evidence of a relationship of the initial curve magnitude, curve type, IBC, age, sex, and curve apex with overcorrection nighttime bracing success or failure is conflicting. These findings can assist clinicians in decision making related to overcorrection nighttime bracing for AIS patients. Further research is needed to evaluate predictive factors with conflicting, inconclusive, and limited evidence of their impact on overcorrection nighttime bracing outcomes for AIS patients.
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Notes
Author Contributions
The idea for the article: TB, VM, AS; the literature searches: MK, MS, TB; data extraction: TB, VM, MK; writing–original draft preparation: TB, VM, AS, MK, MS; and critically revised the work: TB, VM, AS, MK, MS, JPN, JAC.
Table 1
Study characteristics
| Authors (yr) | Design | No. of patients | Age (yr) at initiation of bracing (mean) | Risser sign | Initial curve magnitude | Curve type (no.) | Type of brace | In-brace correction (%) | Brace treatment length (mo) | Months of follow-up (mean) | Definition treatment failure | Definition treatment success |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | Prospective | 102 | 10–16.6 (13.1) | 0–2 | 20–42 | Thoracic (24); lumbar (18); thoracolumbar (14); double (46) | Providence | Thoracic (94); lumbar (103); thoracolumbar (111); double major (90) | ≥24 | 25–81 (30) | Progression ≥6° or spinal fusion | Progression ≤5° |
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | Retrospective | 56 | 10–18 (12.26) | 0–2 | 25–40 | Thoracic (21); lumbar/thoracolumbar (23); double (12) | Providence | 88.3 | >24 | 24.1 | Progression beyond 45° or spinal fusion | Progression <5° |
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Retrospective | 34 | 10–15 | 0–2 | 20–40 | Thoracic (17); lumbar/thoracolumbar (9); double (8) | Providence | 90 | 12 | >12 | Progression >5°, beyond 45° or spinal fusion | NP |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | Retrospective | 63 | 10–16 (13.3) | 0–2 | 25–40 | Thoracic (37); lumbar (5); thoracolumbar (12); double (9) | Providence | 95 | ≥24 | 24 | Progression ≥6°, ≥45° or spinal fusion | Progression ≤5° |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [51] (2019) | Retrospective | 40 | 12.1–13.5 (12.6) | 0–2 | 25–40 | Thoracic (40) | Providence | 68 | >24 | 25 | Progression ≥45° or spinal fusion | Progression ≤5° |
| Lee et al. [38] (2012) | Retrospective | 95 | 10.3–16.5 (13.3) | 0–2 | 25–40 | Thoracic (37); lumbar (5); thoracolumbar (12); double (9) | Charleston | NP | 32.8 | 24–130 (46) | Progression ≥6°, ≥45° or spinal fusion | NP |
| Katz et al. [34] (1997) | Retrospective | 166 | 10.1–16.6 (12.9) | 0–2 | 25–45 | Double major-primary thoracic (34); double major-primary thoracolumbar or lumbar (9); single thoracic (25); single thoracolumbar or lumbar (29); all others (57) | Providence | 83 | 25.2 | 4–51 (17) | Progression >5° or spinal fusion | Progression <5° |
| Simony et al. [39] (2019) | Prospective | 80 | 13.36 | NP | 20–45 | NP | Providence | 100 | 10–36 (18) | 12 | Curve progression ≥5° or spinal fusion | No progression or a slight reduction of the curve |
| Trivedi et al. [41] (2001) | Retrospective | 42 | 10–15.1 (12.5) | 0–1 | 25–40 (30.3) | Thoracic (17); lumbar (3); thoracolumbar (22) | Charleston | 114 | Successful group:13–139 (40); unsuccessful group: 6–86 (36) | NP | Curve progression >5° or necessary to change to full-time bracing | Progression <5° |
Table 2
Methodological quality assessment criteria
Table 3
Quality assessment of the included studies
| Included studies | Items of quality assessmenta) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | Total score | Quality | |
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | Low |
| D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9 | High |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | High |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [51] (2019) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | High |
| Katz et al. [34] (197) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 10 | High |
| Lee et al. [38] (2012) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | Low |
| Simony et al. [39] (2019) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | Low |
| Trivedi et al. [41] (2001) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | Low |
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9 | High |
a) The items are shown in Table 2.
Table 4
Clinical and radiographic parameters for outcome of the brace treatment
| Variable | Study | Study quality | Assessment approach | Significance level | Association with treatment success | Level of evidence for treatment success | Association with treatment failure | Level of evidence for treatment failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial curve magnitude | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Radiography | NP | - | Conflicting | NE | Conflicting |
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Radiography | p=0.31 | NE | NR | |||
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Radiography | p>0.43; OR, 0.99 | NR | NR | |||
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [51] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.024; OR, 0.61 | NE | + | |||
| Katz et al. [34] (1997) | High | Radiography | NP | - | + | |||
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.09 | - | + | |||
| Lee et al. [38] (2012) | Low | Radiography | p=0.64 | NR | NE | |||
| Simony et al. [39] (2019) | Low | Radiography | p<0.001 | NR | + | |||
| Trivedi et al. [41] (2001) | Low | Radiography | p=0.23 | NR | NE | |||
| Curve type | Lee et al. [38] (2012) | Low | Radiography | p=0.79 | NR | Inconclusive | NE | Conflicting |
| Trivedi et al. [41] (2001) | Low | Radiography | p=0.13 | NR | NE | |||
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Radiography | p=0.005 | NE | + | |||
| Katz et al. [34] (1997) | High | Radiography | NP | + | + | |||
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.07 | NE | NR | |||
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Radiography | p=0.45 | NE | NR | |||
| In-brace correction | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Radiography | p=0.01 | + | Conflicting | NE | Conflicting |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Radiography | p=0.009 | + | NE | |||
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.19 | NR | NR | |||
| Katz et al. [34] (1997) | High | Radiography | p=0.0001 | + | - | |||
| Simony et al. [39] (2019) | Low | Radiography | NP | + | - | |||
| Trivedi et al. [41] (2001) | Low | Radiography | p=0.60 | NR | NR | |||
| Curve flexibility | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Radiography | p=0.01 | + | Strong | NE | No association: limited |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Radiography | p=0.013; OR, 0.95 | + | NR | |||
| Age | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Continues | NP | + | Conflicting | NE | Conflicting |
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Continues | p>0.4; OR, 0.80 | NR | + | |||
| Ohrt-Nissen et al. [51] (2019) | High | Continues | p=0.38; OR, 0.84 | NE | NR | |||
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Categorized | p=0.25 | NE | NR | |||
| Risser sign | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Radiography | p=0.05 | + | Strong | NE | Strong |
| Lee et al. [38] (2012) | Low | Radiography | p=0.29 | NR | NE | |||
| Katz et al. [34] (1997) | High | Radiography | NP | + | - | |||
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.01 | + | - | |||
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Radiography | p=0.10 | NE | NR | |||
| Premenarchal status | Ohrt-Nissen et al. [35] (2016) | High | Pre/post menarche | p=0.002 | NE | - | + | Moderate |
| Compliance | Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Self-reported | p=0.04 | NE | - | - | Inconclusive |
| Curve apex | D’Amato et al. [8] (2001) | High | Radiography | p=0.03 | + | Conflicting | NE | Conflicting |
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Radiography | p=0.01 (for association with treatment success); p=0.004 (for association with treatment failure) | + (for T10–L3) | + (for T6–T9) | |||
| Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Radiography | p=0.16 | NE | NR | |||
| Lee et al. [38] (2012) | Low | Radiography | p=0.11 | NR | NE | |||
| Sex | Bohl et al. [37] (2014) | Low | Male-female | p=0.01 | NE | Conflicting | + | Conflicting |
| Davis et al. [33] (2019) | High | Male-female | p=0.17 | NR | NR |
References
2. Konieczny MR, Senyurt H, Krauspe R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Child Orthop 2013;7:3–9.



3. Little DG, Song KM, Katz D, Herring JA. Relationship of peak height velocity to other maturity indicators in idiopathic scoliosis in girls. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:685–93.


4. Lonstein JE, Carlson JM. The prediction of curve progression in untreated idiopathic scoliosis during growth. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984;66:1061–71.


5. Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, Dobbs MB. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. N Engl J Med 2013;369:1512–21.



6. Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord 2018;13:3.



7. Korovessis P, Zacharatos S, Koureas G, Megas P. Comparative multifactorial analysis of the effects of idiopathic adolescent scoliosis and Scheuermann kyphosis on the self-perceived health status of adolescents treated with brace. Eur Spine J 2007;16:537–46.



8. D’Amato CR, Griggs S, McCoy B. Nighttime bracing with the Providence brace in adolescent girls with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:2006–12.


9. Price CT, Scott DS, Reed FR Jr, Sproul JT, Riddick MF. Nighttime bracing for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with the Charleston Bending Brace: long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop 1997;17:703–7.


10. Allington NJ, Bowen JR. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: treatment with the Wilmington brace: a comparison of full-time and part-time use. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1996;78:1056–62.


11. Emans JB, Kaelin A, Bancel P, Hall JE, Miller ME. The Boston bracing system for idiopathic scoliosis: follow-up results in 295 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1986;11:792–801.

12. Green NE. Part-time bracing of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1986;68:738–42.


13. Peltonen J, Poussa M, Ylikoski M. Three-year results of bracing in scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59:487–90.


14. Labelle H, Dansereau J. Orthotic treatment of pediatric spinal disorders and diseases. Spine State Art Rev 1990;4:239–51.
15. Mac-Thiong JM, Petit Y, Aubin CE, Delorme S, Dansereau J, Labelle H. Biomechanical evaluation of the Boston brace system for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: relationship between strap tension and brace interface forces. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:26–32.


16. Katz DE,Orthoses for spinal deformities. Hsu JD, Michael JW, Fisk JR, editors. AAOS atlas of orthoses and assistive devices. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier; 2008. p.125–39.
17. Ruffilli A, Fiore M, Barile F, Pasini S, Faldini C. Evaluation of night-time bracing efficacy in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review. Spine Deform 2021;9:671–8.


18. Climent JM, Sanchez J. Impact of the type of brace on the quality of life of adolescents with spine deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1999;24:1903–8.


19. Antoine L, Nathan D, Laure M, Briac C, Jean-Francois M, Corinne B. Compliance with night-time overcorrection bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: result from a cohort follow-up. Med Eng Phys 2020;77:137–41.


20. Price CT, Scott DS, Reed FE Jr, Riddick MF. Nighttime bracing for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with the Charleston bending brace: preliminary report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1990;15:1294–9.

21. Sattout A, Clin J, Cobetto N, Labelle H, Aubin CE. Biomechanical assessment of Providence nighttime brace for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform 2016;4:253–60.


22. Clin J, Aubin CE, Parent S, Labelle H. A biomechanical study of the Charleston brace for the treatment of scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E940–7.


23. Van den Bogaart M, van Royen BJ, Haanstra TM, de Kleuver M, Faraj SS. Predictive factors for brace treatment outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a best-evidence synthesis. Eur Spine J 2019;28:511–25.


24. Hawary RE, Zaaroor-Regev D, Floman Y, Lonner BS, Alkhalife YI, Betz RR. Brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: risk factors for failure: a literature review. Spine J 2019;19:1917–25.


25. Italiano A. Prognostic or predictive?: it’s time to get back to definitions! J Clin Oncol 2011;29:4718.


26. Hayden JA, Cote P, Bombardier C. Evaluation of the quality of prognosis studies in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 2006;144:427–37.


27. Lievense AM, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Verhagen AP, Verhaar JA, Koes BW. Prognostic factors of progress of hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Arthritis Rheum 2002;47:556–62.


28. Scholten-Peeters GG, Verhagen AP, Bekkering GE, et al. Prognostic factors of whiplash-associated disorders: a systematic review of prospective cohort studies. Pain 2003;104:303–22.


29. Faraj SS, Holewijn RM, van Hooff ML, de Kleuver M, Pellise F, Haanstra TM. De novo degenerative lumbar scoliosis: a systematic review of prognostic factors for curve progression. Eur Spine J 2016;25:2347–58.


30. Bastick AN, Runhaar J, Belo JN, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. Prognostic factors for progression of clinical osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review of observational studies. Arthritis Res Ther 2015;17:152.



31. Lim KK, Matchar DB, Chong JL, Yeo W, Howe TS, Koh JS. Pre-discharge prognostic factors of physical function among older adults with hip fracture surgery: a systematic review. Osteoporos Int 2019;30:929–38.


32. Furlan AD, Pennick V, Bombardier C, van Tulder M. Editorial Board, Cochrane Back Review Group. 2009 Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:1929–41.


33. Davis L, Murphy JS, Shaw KA, Cash K, Devito DP, Schmitz ML. Nighttime bracing with the Providence thoracolumbosacral orthosis for treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective consecutive clinical series. Prosthet Orthot Int 2019;43:158–62.

34. Katz DE, Richards BS, Browne RH, Herring JA. A comparison between the Boston brace and the Charleston bending brace in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:1302–12.


35. Ohrt-Nissen S, Hallager DW, Gehrchen M, Dahl B. Flexibility predicts curve progression in Providence nighttime bracing of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41:1724–30.


36. Ohrt-Nissen S, Hallager DW, Gehrchen M, Dahl B. Supine lateral bending radiographs predict the initial in-brace correction of the Providence brace in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41:798–802.


37. Bohl DD, Telles CJ, Golinvaux NS, Basques BA, DeLuca PA, Grauer JN. Effectiveness of Providence nighttime bracing in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthopedics 2014;37:e1085–90.


38. Lee CS, Hwang CJ, Kim DJ, et al. Effectiveness of the Charleston night-time bending brace in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 2012;32:368–72.


39. Simony A, Beuschau I, Quisth L, Jespersen SM, Carreon LY, Andersen MO. Providence nighttime bracing is effective in treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis even in curves larger than 35°. Eur Spine J 2019;28:2020–4.


40. Yrjonen T, Ylikoski M, Schlenzka D, Kinnunen R, Poussa M. Effectiveness of the Providence nighttime bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a comparative study of 36 female patients. Eur Spine J 2006;15:1139–43.



41. Trivedi JM, Thomson JD. Results of Charleston bracing in skeletally immature patients with idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 2001;21:277–80.


42. Cheung KM, Luk KD. Prediction of correction of scoliosis with use of the fulcrum bending radiograph. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997;79:1144–50.


43. Luk KD, Cheung KM, Lu DS, Leong JC. Assessment of scoliosis correction in relation to flexibility using the fulcrum bending correction index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:2303–7.


44. Yao G, Cheung JP, Shigematsu H, et al. Characterization and predictive value of segmental curve flexibility in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2017;42:1622–8.


45. Upadhyay SS, Nelson IW, Ho EK, Hsu LC, Leong JC. New prognostic factors to predict the final outcome of brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:537–45.


46. He C, Wong MS. Spinal flexibility assessment on the patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a literature review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018;43:E250–8.

47. Cheung JP, Yiu KK, Vidyadhara S, Chan PP, Cheung PW, Mak KC. Predictability of supine radiographs for determining in-brace correction for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018;43:971–6.


48. Rodrigues LM, Ueno FH, Gotfryd AO, Mattar T, Fujiki EN, Milani C. Comparison between different radiographic methods for evaluating the flexibility of scoliosis curves. Acta Ortop Bras 2014;22:78–81.



50. Sanders JO, Khoury JG, Kishan S, et al. Predicting scoliosis progression from skeletal maturity: a simplified classification during adolescence. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:540–53.


51. Ohrt-Nissen S, Lastikka M, Andersen TB, Helenius I, Gehrchen M. Conservative treatment of main thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: full-time or nighttime bracing? J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2019;27:2309499019860017.


-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ
-
Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review2019 June;13(3)