|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 12(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
To clarify the difference in position of the psoas muscle between adult spinal deformity (ASD) and lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
Overview of Literature
Although it is known that the psoas major muscle deviates in ASD patients, no report is available regarding the difference in comparison with LSS patients.
Methods
This study investigates 39 patients. For evaluating spinal alignment, pelvic tilt (PT), pelvic incidence (PI), sacral slope, lumbar lordosis (LL), PI–LL, Cobb angle, and the convex side, the lumbar curves were measured. For measuring the position of the psoas major at the L4/5 disk level, magnetic resonance imaging was used. The displacements of psoas major muscle were measured separately in the anterior–posterior and lateral directions. We examined the relationship between the radiographic parameters and anterior displacement (AD) and lateral displacement (LD) of the psoas major muscle.
Results
AD was demonstrated in 15 cases with ASD and nine cases with LSS (p>0.05). LD was observed in 13 cases with ASD and no cases with LSS (p<0.01). The Cobb angle was significantly greater in cases with AD than in those without AD (p=0.04). PT, LL, PI–LL, and Cobb angle were significantly greater in cases with LD (p<0.05). All cases with LD had AD, but no case without AD had LD (p<0.001). The side of greater displacement at L4/5 and the convex side of the lumbar curve were consistent in all cases.
The numbers of patients with degenerative kyphosis and kyphoscoliosis has increased as the population rapidly ages. Although detailed pathology of kyphoscoliosis is unclear, degenerative changes in the muscles, intervertebral discs, and vertebral bodies result in degenerative kyphosis and kyphoscoliosis [1]. The psoas major muscles are assumed to control the lumbar spine because of their proximity to this region and to the hip joint [2]. With the spread of lateral lumbar interbody fusion, several studies have elucidated the relationship of the psoas major muscle and vertebral bodies [345678]. During lateral lumbar interbody fusion, particularly of L4/5, the anterior displacement (AD) of the psoas major muscle is a risk factor for nerve complications [9]. When the spinal alignment shifts, the psoas major position also shifts for accommodating the altered spinal alignment, because of its lumbar spine insertion. The relationship between spinal alignment and psoas major position has not been researched upon, particularly in cases of adult spinal deformity (ASD) in which alignment changes can occur in both the sagittal and coronal planes. We hypothesized that the psoas major may be displaced when the pelvis and lumbosacral alignment deteriorates. This study aimed at clarifying the difference in psoas muscle position between cases with ASD and lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
This was a retrospective, single-center, and observational study conducted at the Okayama University Hospital, Okayama, Japan. This study was approved by the ethics committee at Okayama University Hospital (approval no., 1608-502-001). Consent was obtained from all patients, and an option to refuse was set up on our homepage.
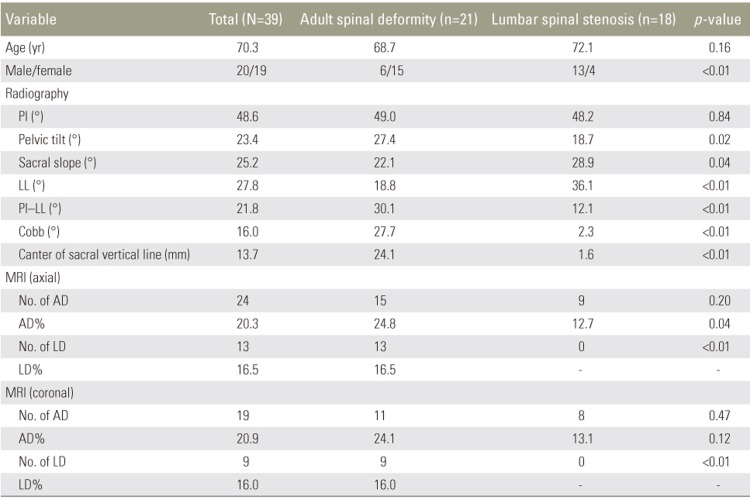
Totally, 39 patients (mean age, 70.2 years; 20 males, 19 females) that underwent surgical treatment at our department between January 2014 and June 2015 were included in this study. The diagnosis was ASD in 21 cases and LSS in 18 cases. ASD was defined when patients complained of low back pain and difficulty in maintaining posture because of spinal deformity. Among the 21 ASD patients, 20 presented with scoliosis defined by a Cobb angle of ≥10°. The remaining patient presented with sagittal malalignment. LSS was defined when patients presented with intermittent claudication and/or nerve root symptoms because of the narrowing of the spinal canal and no evident deformation on radiography, such as scoliosis in the coronal plane or kyphosis in the sagittal plane. Patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis, remnant idiopathic scoliosis, vertebral compression fracture, lumbarization, sacralization, and postural reflex disorders, such as Parkinson's syndrome, were excluded from the study.
We hypothesized that the psoas major position was affected by a spinal alignment change in patients with ASD. We examined the spinal alignment and psoas muscle position as follows. Pelvic tilt (PT), pelvic incidence (PI), sacral slope (SS), lumbar lordosis (LL), and PI–LL were measured using whole spine radiography for evaluating the sagittal plane. The following items were also analyzed using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images at the L4/5 intervertebral disk levels prior to surgery: (1) presence of AD, presence of the psoas major (AD was defined when the psoas major is away from tangent line of the posterior L4/5 intervertebral disk); (2) anteroposterior diameter of the intervertebral disk (mm); and (3) distance from the tangent line posterior of the L4/5 intervertebral disk, to the psoas major posterior end (mm) (Fig. 1). The L4/5 intervertebral disk is the most caudal intervertebral disk through which the psoas major muscle originates. Voyadzis et al. [9] previously used the tangent line of the L4–5 intervertebral disk as a reference line. For adjustment of differences in body size, AD percentage (AD%) was measured as the distance from the tangent line of the posterior L4/5 disk to the posterior edge of the psoas major, divided by the anteroposterior diameter of the L4/5 intervertebral disk.
The Cobb angle, convex side of the lumbar curve, distance of center of apical vertebra to the center of the sacral vertical line (CSVL), and apex vertebra were measured to evaluate coronal alignment with a standing radiograph (Fig. 2). Using T2-weighted MRI images at the L4/5 intervertebral disk level, obtained prior to surgery, the following were measured: (1) presence of lateral displacement (LD) of the psoas major (LD was defined when the psoas major was displaced from the lateral border of intervertebral disk); (2) displacement side when LD was present; (3) horizontal diameter of the disk (mm); and (4) distance from the lateral border of the L4/5 intervertebral disk to the medial end psoas major at L4/5 (mm). LD percentage (LD%) was calculated as the distance from the lateral edge of the L4/5 intervertebral disk to the medial edge of the psoas major, divided by the disk horizontal diameter of the L4/5 intervertebral disk. Patients were categorized based on the presence of AD and LD, and each parameter was compared. The relationships between the displacement presence or quantity of the psoas major and radiographic parameters were also examined.
Fisher's exact test evaluated the ratio between the two groups. Student t-test compared the average values between the two groups, and one-way analysis of variance compared the average values among the three groups. Pearson's correlation test was used to assess the correlation of each measurement. All statistical analyses were performed using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan).
Totally, 39 patients that underwent surgical treatment at our department between January 2014 and June 2015 were included in this study. No significant differences in age were observed between the ASD and LSS group. The percentage of women with ASD was significantly greater than that with LSS (Table 1). The average PI was not significantly different between the ASD and LSS group. The average PT, SS, LL, and PI–LL were significantly different between the ASD and LSS group. The CSVL distance and apical vertebra was also significantly different between the two groups. Twenty-four cases presented with AD on MRI (15 in the ASD group, nine in the LSS group), and the percentage of those with AD was significantly higher in the ASD group than the LSS group. The mean AD% was 24.8% in the ASD group and 12.7% in the LSS group; the difference between the two groups was statistically significant. LD was observed in 13 cases, all of which were cases of ASD.
The patients were categorized into two groups based on the presence of AD and LD and each parameter was compared (Table 2). The Cobb angle was significantly greater in the AD group compared with that without AD. The PT, LL, PI–LL, and Cobb angle were significantly greater in the LD group compared with that without LD.
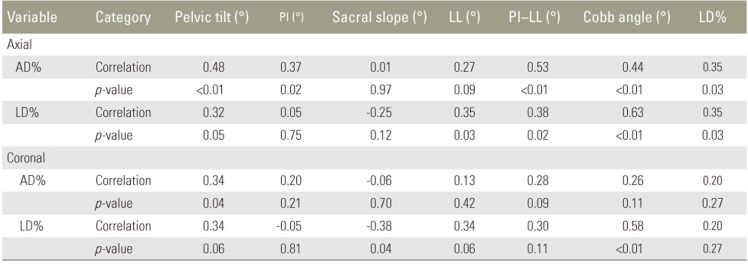
AD% was correlated to PT, PI, PI–LL, and Cobb angle with correlation coefficients being 0.48, 0.37, 0.53, and 0.44, respectively (Table 3), whereas, LD% was correlated to PT, LL, PI–LL, and Cobb angle, with correlation coefficients being 0.32, 0.38, 0.41, and 0.71, respectively.
In 13 patients with LD, the relationship between the psoas major displacement side at the L4/5 intervertebral disk level in MRI and the convex direction of the lumbar curve on radiography was examined. The psoas major muscle displacement direction was the same as that of the convex side of the lumbar curve.
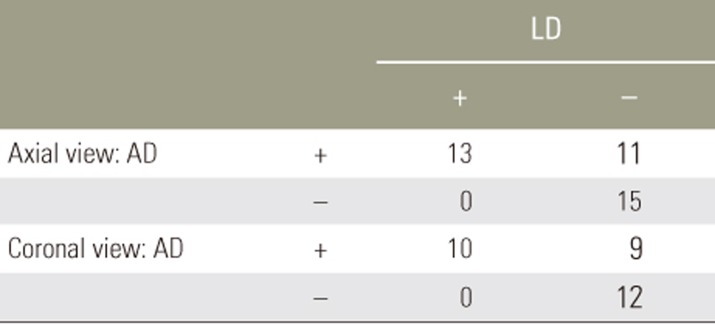
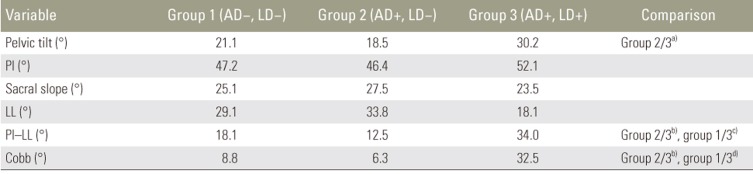
The cases with a combination of AD and LD are shown in Table 4. All cases with LD had AD as well, but no case without AD had LD. Further studies were performed by categorizing the patients into three groups: 15 without AD or LD (group 1), 11 with AD and without LD (group 2), and 13 with both AD and LD (group 3). A comparison of parameters among the three groups showed significant differences in PT and PI–LL (Table 5). No significant differences were observed between groups 1 and 2; groups 2 and 3 showed significant differences in PT, PI–LL, and Cobb angle.
The psoas major muscle consists of fascicles originating from five vertebral bodies (L1–L5), four intervertebral discs (L1/2–L4/5), and five transverse processes (L1–L5) [10]. Each fascicle gets inserted into the femoral lesser trochanter after exiting the iliopubic eminence. A previous study reported that each muscle belly length is almost similar (±0.5 mm), even though their origins vary [11]. The psoas major is widely known as a hip flexor [12] and stabilizes the lumbar spine through compression [13]. The function of the psoas major muscle differs among the fascicles; the muscle fascicle originating from the transverse process acts as an extensor, whereas, the muscle fascicle originating from the vertebral body and intervertebral disk acts as a flexor [14]. Side bending is a common function. When the lumbar spine bends forward, the fascicles become shorter on the cranial side than on the caudal side [11]. The changes in the length of the fascicles originating from the L1 vertebral body and L5 transverse process are −14±9 mm and 0±2 mm, respectively.
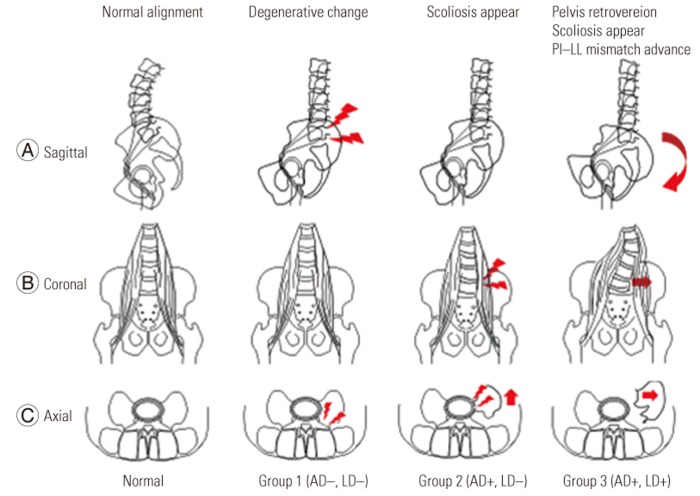
We hypothesized that psoas major position is affected by changes in spinal alignment in patients with ASD (Fig. 3). Because degenerative changes in spinal alignment are likely to occur first in the sagittal plane, the first major psoas muscle change is assumed to be AD. When deterioration in the sagittal plane is observed, the fascicles originating from the transverse process are damaged prior to fascicles originating from other parts (group 1 in Fig. 3), and psoas major AD is observed (group 2 in Fig. 3). The convex side of the apical vertebra is similar to the side of the lumbar concavity at the L4/5 intervertebral disk level. Apical vertebra translation may lead to a larger fascicle tension force on the concave side at the L4/5 intervertebral disk level. This large tension force gradually disrupts the medial attachment of the psoas muscle to the vertebral body and disk, namely, LD (group 3 in Fig. 3).
In the present study, although there were no significant differences in the sagittal parameters either in the presence or absence of AD, the amount of AD of the psoas major on MRI correlated with PT, PI, PI–LL, and Cobb angle. Furthermore, when the psoas major was displaced away from the L4/5 intervertebral disk (LD), both sagittal alignment and coronal alignment worsened. Patients with LD had significantly greater Cobb angles, and a strong correlation (R=0.63) was observed between the distance from the L4/5 intervertebral disk to the medial border of the psoas major and the Cobb angle. The results of the present study support our hypothesis. AD preceded LD in all cases. The psoas major originating at the L4/5 intervertebral disk level correlated with the coronal alignment. It is suggested that coronal alignment deterioration corresponds to LD.
Patients with spondylolisthesis were excluded from this study because the anterior slippage of L4 might increase the AD% and the psoas major may get damaged. Patients with compression fractures and idiopathic scoliosis were also excluded because these conditions possess certain, but different, influences on the psoas muscle position. A previous study reported a psoas sign in a lumbarization case; thus, lumbarization should be considered as an inclusion criteria.
The present study involves a concern regarding the magnitude of error when using MRI for measurement. In previous studies where MRI was used to measure muscles, the intra-class correlation coefficients ranged from 0.832 to 0.99 [151617181920]. Reports on intra-observer and inter-observer errors in muscle measurement using CT and MRI also exist [21]. The reliability was found to be acceptable. Additionally, the authors encouraged unifying image modalities for research-based measurements of target muscles. The present study only includes MRI data and not CT data. Therefore, we believe that the reliability is acceptable, as reported in previous studies.
The small sample size and retrospective design are the limitations of this study. A prospective and longitudinal analysis with a large sample size is required to further prove our hypothesis.
The relationships between the psoas major muscle positions and spinal alignments in ASD and LSS patients were examined. VD of psoas major muscle was observed in both LSS and ASD patients, whereas LD of psoas major muscle was observed only in ASD patients. The extent of psoas major muscle ventral displacement was correlated with the worsening of the sagittal parameter and the significant deterioration of the sagittal and coronal parameters was observed in patients with psoas major muscle LD.
Notes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, Miyamoto M, Miyatake Y. Lumbar degenerative kyphosis: clinical, radiological and epidemiological studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988 13:1317–1326. PMID: 2974629.


2. Santaguida PL, McGill SM. The psoas major muscle: a three-dimensional geometric study. J Biomech 1995 28:339–345. PMID: 7730392.


3. Benglis DM, Elhammady MS, Levi AD, Vanni S. Minimally invasive anterolateral approaches for the treatment of back pain and adult degenerative deformity. Neurosurgery 2008 63(3 Suppl): 191–196. PMID: 18812924.


4. Davis TT, Bae HW, Mok JM, Rasouli A, Delamarter RB. Lumbar plexus anatomy within the psoas muscle: implications for the transpsoas lateral approach to the L4-L5 disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011 93:1482–1487. PMID: 22204003.


5. Kepler CK, Bogner EA, Herzog RJ, Huang RC. Anatomy of the psoas muscle and lumbar plexus with respect to the surgical approach for lateral transpsoas interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 2011 20:550–556. PMID: 20938787.


6. Le TV, Burkett CJ, Deukmedjian AR, Uribe JS. Postoperative lumbar plexus injury after lumbar retroperitoneal transpsoas minimally invasive lateral interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013 38:E13–E20. PMID: 23073358.


7. Regev GJ, Chen L, Dhawan M, Lee YP, Garfin SR, Kim CW. Morphometric analysis of the ventral nerve roots and retroperitoneal vessels with respect to the minimally invasive lateral approach in normal and deformed spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009 34:1330–1335. PMID: 19455010.


8. Uribe JS, Arredondo N, Dakwar E, Vale FL. Defining the safe working zones using the minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg Spine 2010 13:260–266. PMID: 20672964.


9. Voyadzis JM, Felbaum D, Rhee J. The rising psoas sign: an analysis of preoperative imaging characteristics of aborted minimally invasive lateral interbody fusions at L4-5. J Neurosurg Spine 2014 20:531–537. PMID: 24606002.


10. Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse M. Quantitative anatomy of the lumbar musculature. J Biomech 1999 32:311–316. PMID: 10093031.


11. Bogduk N, Pearcy M, Hadfield G. Anatomy and biomechanics of psoas major. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 1992 7:109–119.


12. Gary H, Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH. Gray's anatomy. 37th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1989.
13. Janevic J, Ashton-Miller JA, Schultz AB. Large compressive preloads decrease lumbar motion segment flexibility. J Orthop Res 1991 9:228–236. PMID: 1992073.


14. Park RJ, Tsao H, Cresswell AG, Hodges PW. Differential activity of regions of the psoas major and quadratus lumborum during submaximal isometric trunk efforts. J Orthop Res 2012 30:311–318. PMID: 21800359.


15. Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, Lee HY. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005 30:123–129. PMID: 15626992.


16. Barker KL, Shamley DR, Jackson D. Changes in the cross-sectional area of multifidus and psoas in patients with unilateral back pain: the relationship to pain and disability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004 29:E515–E519. PMID: 15543053.


17. Ranson CA, Burnett AF, Kerslake R, Batt ME, O’Sullivan PB. An investigation into the use of MR imaging to determine the functional cross sectional area of lumbar paraspinal muscles. Eur Spine J 2006 15:764–773. PMID: 15895259.


18. Gille O, Jolivet E, Dousset V, et al. Erector spinae muscle changes on magnetic resonance imaging following lumbar surgery through a posterior approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007 32:1236–1241. PMID: 17495782.


19. Hides JA, Belavy DL, Stanton W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of trunk muscles during prolonged bed rest. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007 32:1687–1692. PMID: 17621220.


20. Fan S, Hu Z, Zhao F, Zhao X, Huang Y, Fang X. Multifidus muscle changes and clinical effects of onelevel posterior lumbar interbody fusion: minimally invasive procedure versus conventional open approach. Eur Spine J 2010 19:316–324. PMID: 19876659.


21. Hu ZJ, He J, Zhao FD, Fang XQ, Zhou LN, Fan SW. An assessment of the intra- and inter-reliability of the lumbar paraspinal muscle parameters using CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011 36:E868–E874. PMID: 21224757.


Fig. 1
(A, B) Measurement parameters in the axial plane at L4/5 level. PM, psoas muscle; D, L4/5 intervertebral disk; L, lamina; M, multifidus muscle; E, erector spinae muscle; line 1, tangent line of posterior of L4/5 disk; line 2, transverse diameter of L4/5 disk; line 3, anteroposterior diameter of L4/5 disk; line 4, distance from lateral border of L4/5 disk to medial border of PM; line 5, distance from tangent line of posterior of L4/5 disk to posterior of PM.
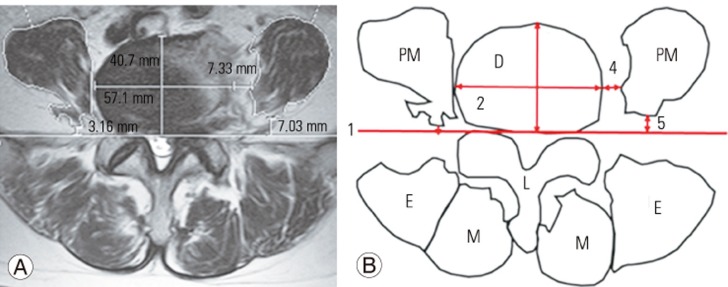
Fig. 2
(A, B) Measurement parameters in the coronal plane in lumbar spine. CSVL, center of sacral vertical line; arrow 1, direction of lumbar curve; line 2, Cobb angle; line 3, distance from apex to CSVL.
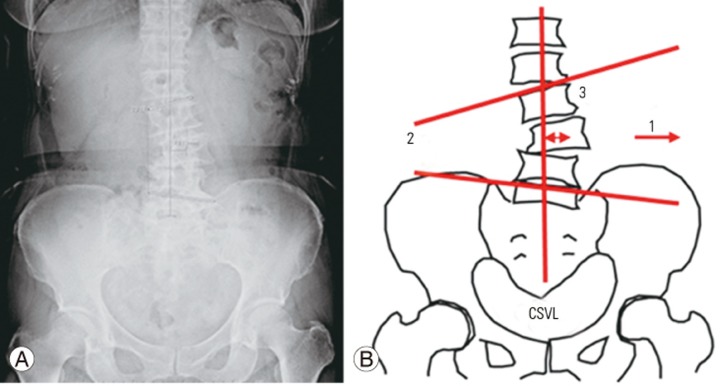
Fig. 3
(A–C) Relationship between psoas major muscle displacement and spinal alignment. Age-related changes cause sagittal plane alignment deterioration. Mild scoliosis progress in accordance with AD. Further alignment is exacerbated by LD. AD, anterior displacement of the psoas major muscle; LD, lateral displacement of the psoas major muscle; PI, pelvic incidence; LL, lumbar lordosis.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 1 Scopus
- 5,496 View
- 90 Download
- Related articles in ASJ